Lit of the Week – 3/15/16
Clinical question / background:
- Definitions of sepsis and septic shock were last revised in 2001
- SIRS criteria have been criticized for lack of specificity and inadequate representation of the patient with sepsis
- NEJM in 2015 – SIRS misses 1/8 septic patients
- Better understanding of sepsis inappropriate immune response to infection causing life-threatening organ damage vs a continuum of inflammation
- Dysregulated host response = both pro and anti inflammatory factors
- Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) and the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM) redefined sepsis with the Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3)
Design:
- 19-member task force; Critical care, ID, Surgery, Pulmonary, Anesthesia
- No Emergency Medicine physicians
- For sepsis, retrospective + validation cohort study performed of adult patients with suspected infection
- UPMHC Health Care System, Kaiser Permanente, U.S. VA System, Kings County Washington Hospitals, 1 German Hospital
- Outcomes: Hospital mortality and overall mortality, ICU stay of 3 days or longer, or both
- Compared area under ROC curve for SIRS, SOFA, and LODS (Logistic Organ Dysfunction System)
- For septic shock, systemic review and Delphi consensus process to identify 3 variables (Hypotension, Elevated lactate, need for pressor) that correlated with mortality
- Retrospective and validation cohort study
- Outcome: in-hospital mortality
New Definitions:
- Sepsis
- Life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection
- Suspected / Documented Infection AND
- Organ Dysfunction identified as an rise in total SOFA score ≥ 2 as a consequence of infection
- SOFA score assesses Six Organ Systems — CNS, CV, Respiratory, Liver, Renal, Coagulation
- Baseline SOFA 0 assumed in healthy patients
- SOFA MDCalc
- Overall mortality 10% (mortality from STEMI is ~8%)
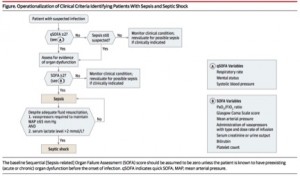
- Potential septic patients identified with ≥ 2 qSOFA criteria
- Hypotension (SBP ≤ 100 mm Hg), Altered Mental Status (GCS < 15 or subjective determination), Tachypnea (RR ≥ 22/min)
- qSOFA MDCalc
- These patients are at high risk for poor outcome and should be assessed for evidence of organ dysfunction with full SOFA and measurement of lactate
- Septic Shock
- Subset of sepsis in which underlying circulatory and cellular metabolism abnormalities are profound enough to substantially increase mortality
- SEPSIS + Vasopressors to maintain MAP ≥ 65 AND Lactate > 2 mmol/L after adequate fluid resuscitation
- Fluid resuscitation not defined objectively
- In hospital mortality ~42%
- SEPSIS + Vasopressors to maintain MAP ≥ 65 AND Lactate > 2 mmol/L after adequate fluid resuscitation
- Subset of sepsis in which underlying circulatory and cellular metabolism abnormalities are profound enough to substantially increase mortality
- Organ Dysfunction identified as an rise in total SOFA score ≥ 2 as a consequence of infection
Take-home:
- Patient with suspected infection
- A qSOFA Score of ≥2 suggests a high risk of poor outcome; these patients should be assessed for evidence of organ dysfunction, including lactate levels
- They should also have a SOFA Score calculated (with a SOFA Score ≥2 meeting criteria for the new clinical definition of sepsis, as a proxy for organ dysfunction)
- Patients should receive standard interventions for sepsis, including but not limited to adequate fluid resuscitation, antibiotics, and source control
- If SOFA score of ≥2, and after correcting for hypovolemia, pressors are required to keep MAP ≥ 65 mm Hg and measured lactate > 2 mmol/L, patient is in septic shock
- Sayonara to SIRS and Severe Sepsis
Strengths:
- Data-driven with large patient cohorts supporting clinical criteria for definitions
- Simple clinical criteria with the qSOFA to identify patients without lab tests who may be at risk for poor outcomes (i.e. prolonged ICU course and death) in the presence of infection
Weaknesses / Critiques
- There is still no known precise pathophysiological feature defining sepsis
- Unclear how to interpret studies (EGDT, ProCESS, PROMISE, ARISE) with new definitions
- Not endorsed by ACEP or SAEM as emergency providers were not included
- qSOFA and SOFA are mortality predictors, NOT designed to be tests for sepsis
- qSOFA has not been prospectively validated
- Compared to SIRS, qSOFA is more specific (but less sensitive) for predicting mortality
- Prospective validation is needed to determine the real-world performance of Sepsis-III
Additional Links / Sources
http://emcrit.org/pulmcrit/problems-sepsis-3-definition/
http://stemlynsblog.org/sepsis-16/
http://icmwk.com/2016/02/25/sepsis-3/