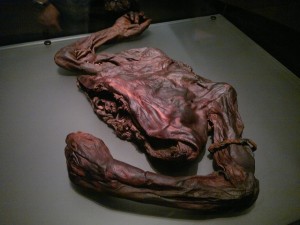
One of the most controversial attractions to have entered and taken root in Atlanta is the BODIES Exhibition. A science based exhibit, the museum of sorts has numerous real human bodies in various poses on display while other sections analyze specific parts or components of the human body and systems such as the brain. Aside from the arguments surrounding the acquirement of the bodies themselves, many drew conflict with the concept of placing someone’s remains on public display. Those arguments have diminished over the years as the angle of the exhibit is pushed to encourage scientific learning and medical education for all levels. BODIES, however, is certainly not the first (or likely last) tourist attraction that has used the human corpse as a means of revenue.
Looking at an earlier, less ominous example brings us to the amusement park Disneyland. Built in the mid-60s, the popular ride attraction “Pirates of the Caribbean” draws in numbers of park visitors. Sitting in a boat, visitors are taken through a bayou-like environment passing many ‘piratical’ scenes. Use of sculptures, audio effects, and animatronics, all bring the pirates and their rambunctious natures alive for guests. Our society today tries to achieve realism in games, films, and other media forms in order to enrapture the viewer in an experience. This same drive was present back in 1967 when Walt Disney and his team of Imagineers (Disney imagine engineers) created the attraction. After having spent so much time and money on the rest of the attraction in terms of props and wardrobes, the fake skeletons of the time paled in comparison to the rest of the environment’s realism. The inclusion of fake, full skeletons and skull cross and bones throughout the ride did not fit and by general consent, the team agreed to put in real human remains in their place. Taking remains from the UCLA Medical Center’s anatomy department, the Disney Imagineers placed skeletons throughout and profited from the parks’ visitors who essentially entered a highly decorated morgue, likely not knowing of the ‘props’ realism.
Disney claims they have fully removed the real human remains and replaced them with actual props (now more easily crafted to look realistic) but some viewers are still skeptical, leading to investigations of the ride. Analysis has shown a couple of skeletal remains were in fact still present in the ride and there are a few more that are still suspected. It’s surprising that once those pieces were found, they were not instantly removed and returned to their proper countries of origin and laid to rest in a proper burial as the others were. Granted, that claim also leads one to question how the remains were identified to belong to a certain country or family if they were previously donated from the medical center.
Regardless of whether Disney has or has not removed all previously living skeletal remains, it’s still disturbing that one not only took the remains of humans who donated their bodies for science but instead put them in a children’s amusement park propped up to look like discarded pirates. At this point, it also does not matter if the bodies were properly returned because the damage is already done. Disney will continue to profit off of the real human remains and it’s lingering legacy as long as people continue to propagate the idea that there are still real skeletons among the fake in the Pirates of the Caribbean attraction.
BODIES: The Exhibit Atlanta website: http://www.premierexhibitions.com/exhibitions/4/48/bodies-exhibition/bodies-exhibition-atlanta
Link to Disney Article: http://www.atlasobscura.com/articles/are-there-still-real-skeletons-in-disneylands-pirates-of-the-caribbean