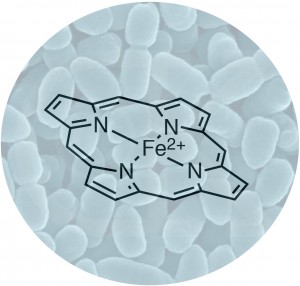
 The ability of heme proteins to reversibly bind diatomic ligands allows organisms to sense changes in their environment. Recently, changes in gaseous ligand concentrations have been proposed to be involved in the pathogenesis of a variety of bacteria. Our work focuses on understanding how the globin coupled sensor protein family senses oxygen and transmits the binding signal into downstream events. Understanding how these diatomic signals are transduced will elucidate the role of heme sensors in bacterial signaling pathways and pathogenesis, as well as potentially yield starting points for the development of novel antibacterial agents. More…
The ability of heme proteins to reversibly bind diatomic ligands allows organisms to sense changes in their environment. Recently, changes in gaseous ligand concentrations have been proposed to be involved in the pathogenesis of a variety of bacteria. Our work focuses on understanding how the globin coupled sensor protein family senses oxygen and transmits the binding signal into downstream events. Understanding how these diatomic signals are transduced will elucidate the role of heme sensors in bacterial signaling pathways and pathogenesis, as well as potentially yield starting points for the development of novel antibacterial agents. More…
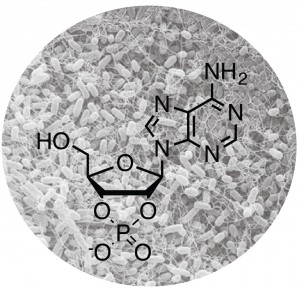
Nucleotides play a number of important roles as second messengers involved in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic signaling. Mounting evidence suggests that there may be additional nucleotide signaling pathways but very little is known about the proteins involved. Our work aims to identify new cyclic nucleotide-dependent pathways in bacteria, including the proteins and signals involved in sensing cNMPs and regulating cNMP levels. These studies provide basic insights into novel cellular signaling pathways and metabolism, as well as the phenotypes controlled by cNMPs. More…
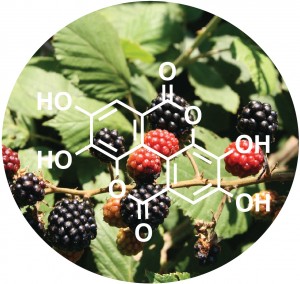
Plant extracts have been used as anti-bacterial agents for centuries, but the active compounds within the extracts are rarely known. Given the rise in antibiotic resistant bacteria and the recent identification of the role of biofilm formation in bacterial infections, identifying novel anti-biofilm compounds is incredibly important. In a collaborative project with Prof. Cassandra Quave, we are working to identify components within plant extracts that have anti-biofilm active and identify synergistic relationships between compounds.