Authors: Changming Qin and Huw M. L. Davies
J. Am. Chem. Soc.,
2014, 136 (27), pp 9792–9796
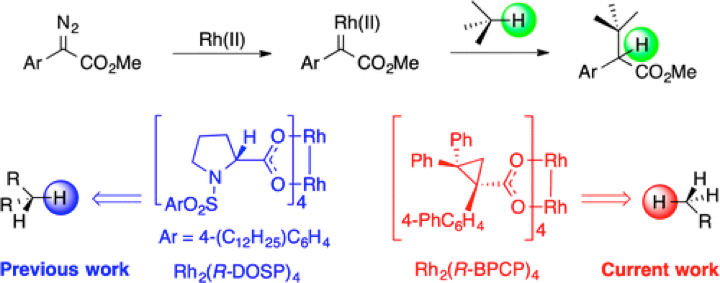
The influence of sterically demanding dirhodium tetracarboxylate catalysts on the site selectivity of C–H functionalization by means of rhodium carbene-induced C–H insertion is described. The established dirhodium tetraprolinate-catalyzed reactions of aryldiazoacetates cause preferential C–H functionalization of secondary C–H bonds as a result of competing steric and electronic effects. The sterically more demanding dirhodium tetrakis(triarylcyclopropanecarboxylate) catalysts, exemplified by dirhodium tetrakis[(R)-(1-(biphenyl)-2,2-diphenylcyclopropanecarboxylate)] [Rh2(R-BPCP)4], favor C–H functionalization of activated primary C–H bonds. Highly site-selective and enantioselective C–H functionalization of a variety of simple substrates containing primary benzylic, allylic, and methoxy C–H bonds was achieved with this catalyst. The utility of this approach has been demonstrated by the late-stage primary C–H functionalization of (−)-α-cedrene and a steroid.